Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) have been a hot topic in the digital art world for a while now. They allow artists and creators to monetize their digital assets in a way that was not possible before. With NFTs, digital assets such as images, videos, and music can be tokenized and sold as unique, one-of-a-kind items.
However, the distribution models for NFTs can vary greatly, with some being more popular than others. It is essential for investors and teams to understand their nuances and to have the right choice. The distribution models represent supply, which should be designed with the expected demand in mind, and they determine the success (or failure) of an NFT project. Why? Let's have a deeper look.
The following blog post will focus on three NFT distribution models: Standard Mint, Free Mint, and Dutch Auctions.
STANDARD MINT
The Standard Mint distribution model is the most popular and common for NFTs. It is a straightforward process where the creator sets a fixed price for their fixed supply of NFTs and sells it through an online marketplace.
This distribution model suits NFT projects across all sectors, including digital collectibles, fundraising, and fixed-price products (e.g., membership subscriptions).
Successful examples are Bored Ape Yacht Club, Doodles, Moonbirds, Tim Ferriss' Cockpunch.
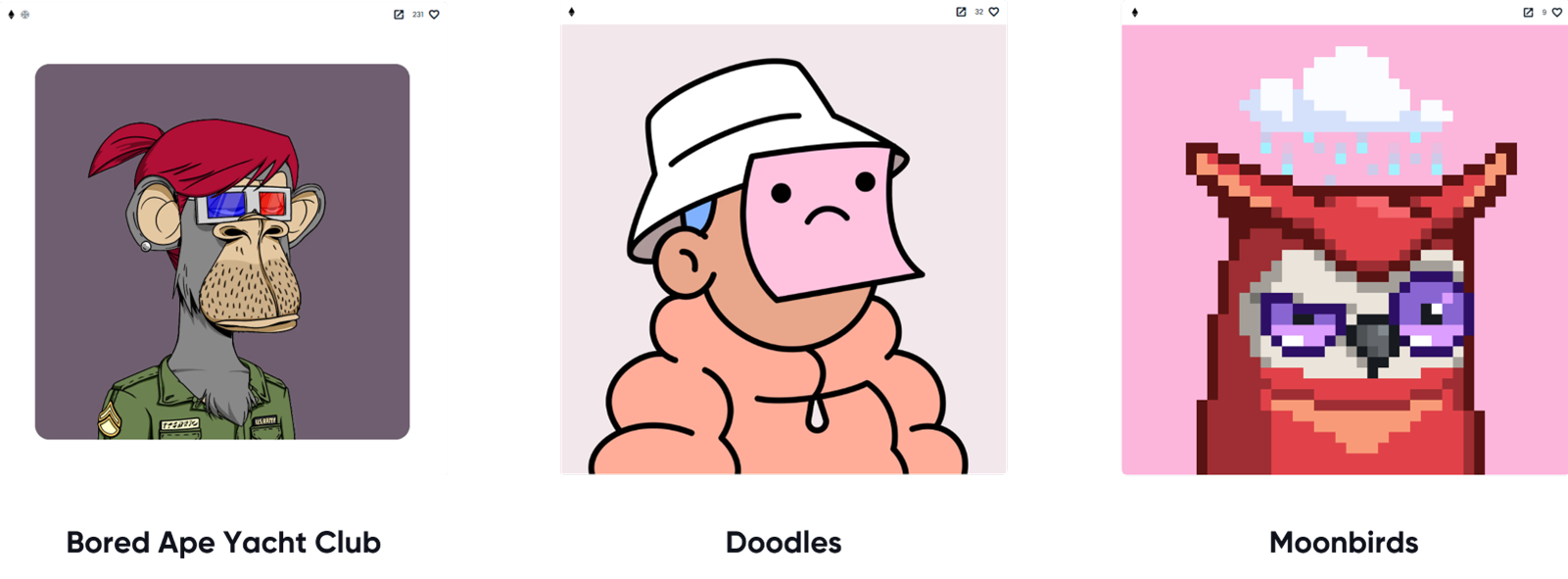
Standard Mint - Two Sides
One advantage of the Standard Mint model is that it is simple and easy to understand. Buyers know what they are paying for and what they will receive. In addition, the creator has control over the price of their NFT and can adjust it as needed to reflect the market demand. The whitelisting process also enables the team to select and control who gets to join the owner community.
However, the downside to the Standard Mint model is that it can be challenging to set a fixed price in advance. If the founders set too high a price, not enough people may mint, while too low a price may lead to speculative trading and fewer funds raised. Moreover, developing a fixed price can be tricky because there are no valuation metrics for NFTs. It is often based on social proof.
FREE MINT
The Free Mint distribution model is a more recent development in the world of NFTs. In this model, the creator gives away a certain number of NFTs for free. The distribution mechanism is similar to standard mints, but the price is 0. The idea is to create a buzz around the NFT and increase its value over time. The creator may also give away a limited number of NFTs as part of a larger sale.
This model is usually suitable for well-funded teams, gaming, and marketing bootstrapping a new community.
Powerful use cases areDigiDaigaku, The Potatoz by Memeland, Bored Ape Kennel, Club (airdrop), CryptoPunks, Rektguy.
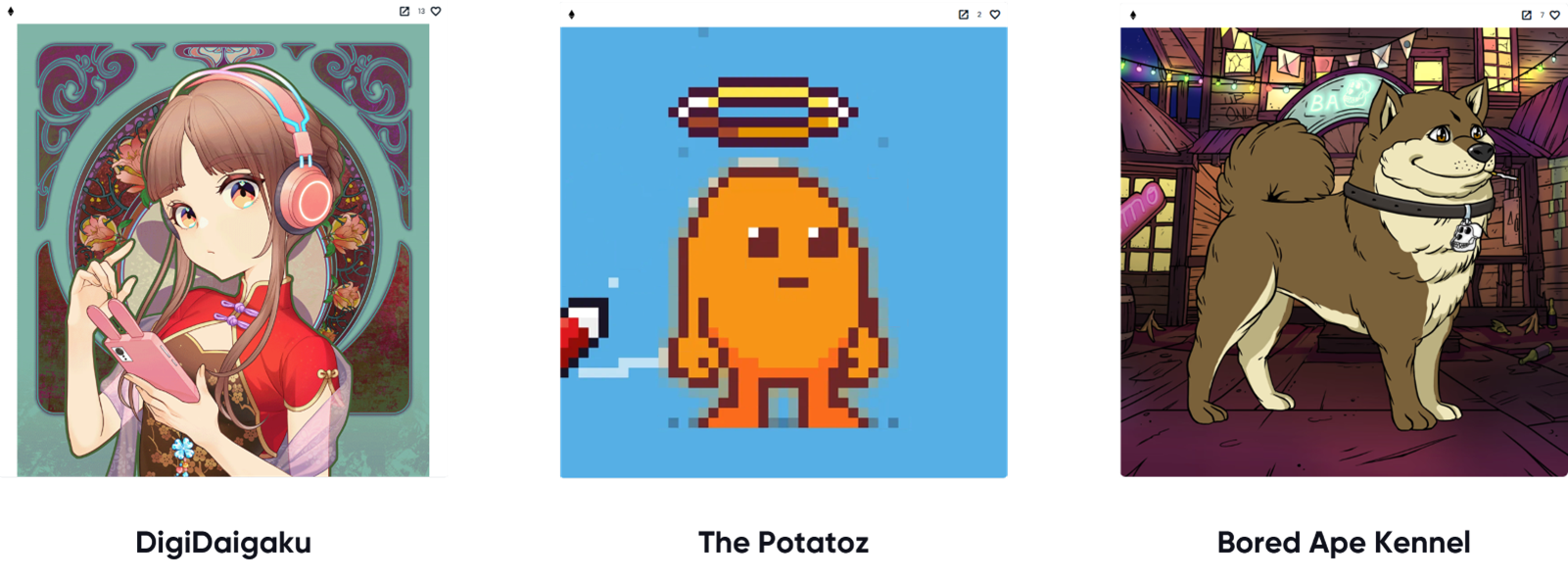
Free Mint - Yes or No?
One advantage of the Free Mint model is that it can effectively build a following and generate interest in an NFT. By giving away NFTs for free, the creator can attract potential buyers who may have yet to be interested in the NFT. Furthermore, if the NFT increases in value over time, the creator may be able to sell additional copies at a higher price, generating a profit. Free Mints are also usually the fastest way to bootstrap an initial community and users.
However, the downside to the Free Mint model is that if launch-related information is not closely secured or the allowlist is unproperly maintained, insiders may mint all the NFTs and sell them for greater prices on the secondary market. There is also a high chance of failing if the team is not well-funded.
DUTCH AUCTIONS
The Dutch Auction distribution model is a unique approach to selling NFTs. In this model, the creator sets a starting high price for their NFT, gradually decreasing over time. Buyers can purchase the NFT at any point during the auction, but the longer they wait, the lower the price will be. The auction ends when a buyer buys the NFT, or the price reaches a predetermined minimum.
Since the model implies the price being based on bids, it is suitable for limited-edition Art collections and projects where demand is higher than supply.
Successful cases: Art Blocks Curated collections, Azuki, QQL Mint Pass, SuperRare'sRarePass.

Dutch Auctions - Pros and Cons
One benefit of the Dutch Auctions model is that it creates a sense of competition among buyers. Because the price is continually decreasing, customers are incentivized to purchase sooner rather than later. Additionally, there is also no need to fix a price upfront because the price range is set. The Dutch Auction model can also help establish a fair market price for an NFT based on supply and demand.
The drawback of the Dutch Auction concept is that it can be challenging to foresee the NFT's final price. Moreover, while they optimize for the highest possible price, it can mean less room for future price appreciation. In addition, the project can face botting if the auction is accessible to the general public. Many Art Blocks Curated collections have made this clear. For instance, due to bots, Skulpuur's Dutch auction swiftly sold out for 5 ETH. Its floor price dropped below the mint price in less than a week.
Making the choice
The best distribution model fit for each project depends on their objectives and needs — whether for fundraising, seeding a community, or marketing. To choose the suitable model for the project, the team should ask itself:
- What will the initial supply be?
A larger supply can potentially bring more funds, but it can be harder to sell out. That's why it is essential to estimate market demand.
- Will it be fixed or dynamic?
Standard mints, for example, mean a fixed collection size and do not let the supply to increase over time.
- What is your key objective? Do you aim for fundraising or not?
While free mints do not raise any funds, Dutch auctions optimize for price discovery.
In conclusion, NFT distribution models vary greatly, each with advantages and disadvantages. We have discussed three popular models, focusing on their particular characteristics. Ultimately, the distribution model choice depends on the goals of the creator and the nature of the NFT being sold. Regardless of it, NFTs have revolutionized the way digital assets are monetized and have opened up new possibilities for artists and creators.
Source: From Dutch Auctions to Open Editions: A Deep Dive Into NFT Distribution Models by Teng Yan
